- Eye Infection During Pregnancy
- Tips You Should Follow For Eye Infection
- Causes Of Eye Infection During Pregnancy
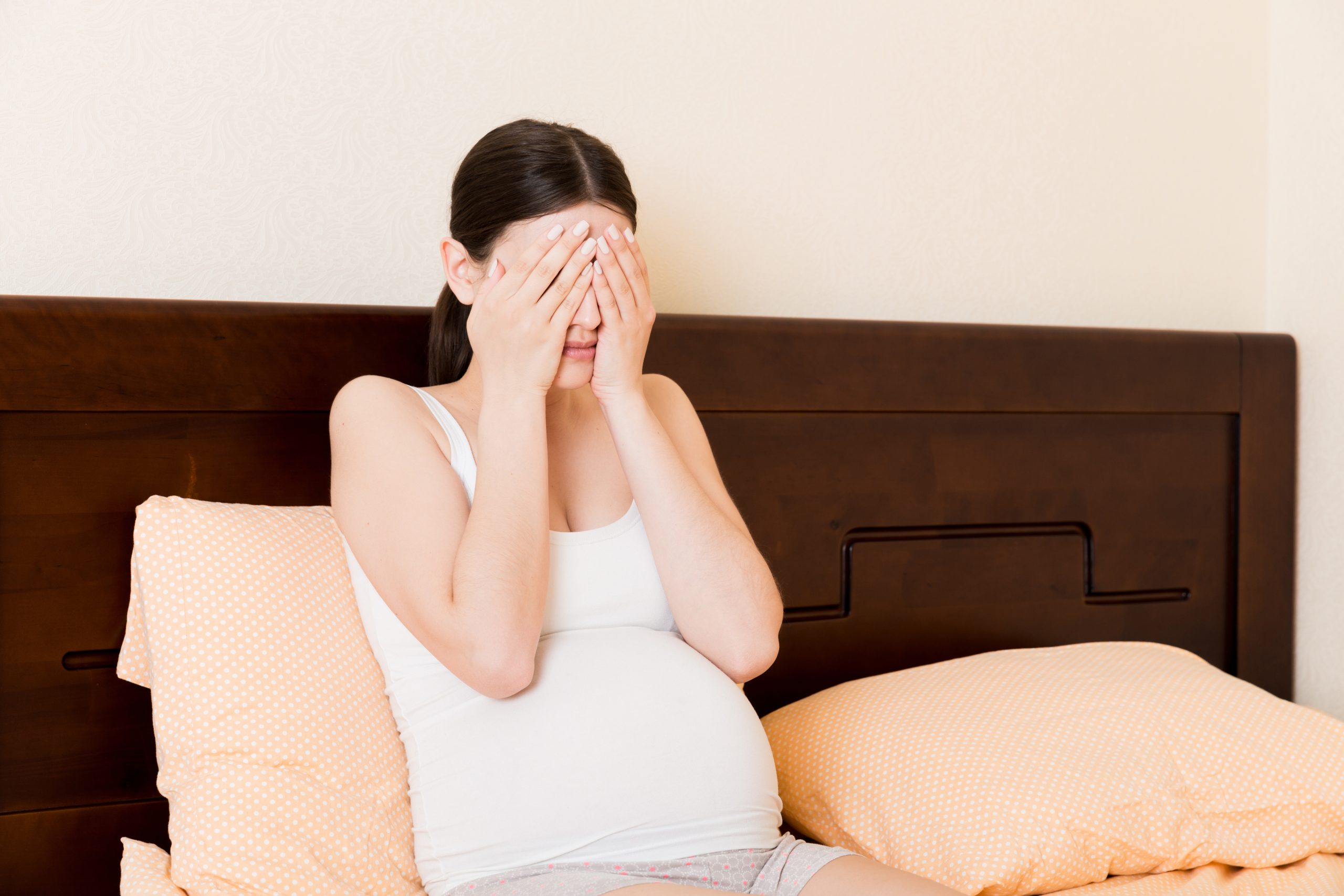
Eye infection during pregnancy can occur due to various factors. Pregnancy can affect the immune system, making women more susceptible to infections in general, including those affecting the eyes. Additionally, hormonal changes during pregnancy can alter the body’s response to infections.

Is Eye Infection During Pregnancy Normal ?
Eye infection during pregnancy is not considered normal, but it can occur due to various factors. Common causes of eye infections during pregnancy include:
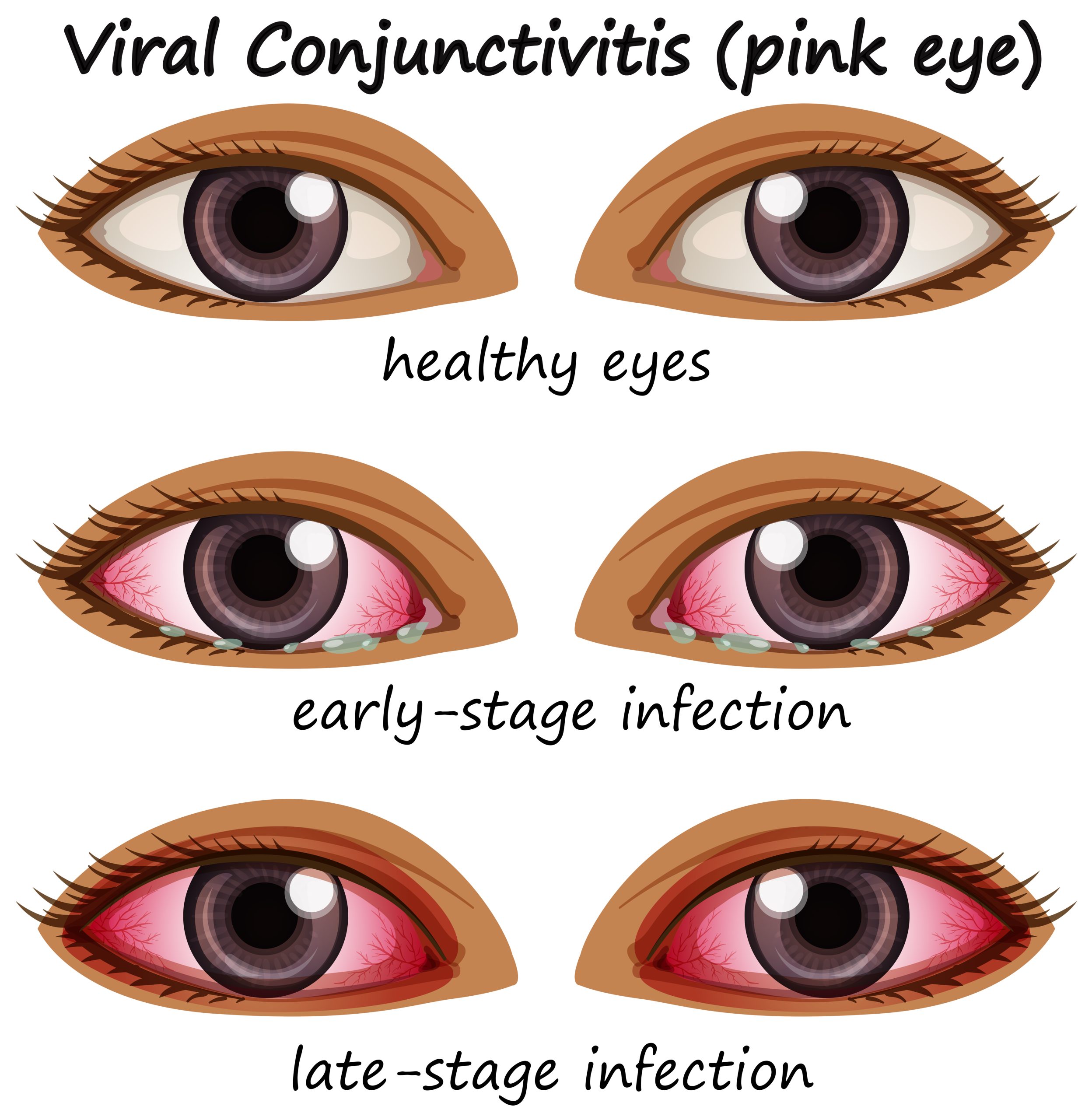
- Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye): Conjunctivitis is inflammation or infection of the conjunctiva, the thin layer of tissue that covers the white part of the eye and lines the inner surface of the eyelids. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, allergens, or irritants. Pregnant women may be at increased risk of developing conjunctivitis due to changes in immune function.
- Stye (Hordeolum): A stye is a red, painful bump that forms on the eyelid, usually near the edge of the eyelid. It is typically caused by a bacterial infection of the oil glands in the eyelid. While pregnancy itself does not cause styes, hormonal changes and immune system alterations may increase the likelihood of developing one.
- Blepharitis: Blepharitis is inflammation of the eyelids, often caused by bacteria or an overgrowth of normal skin bacteria. It can lead to redness, itching, irritation, and crusty eyelids. Pregnancy-related changes in hormone levels may contribute to the development or exacerbation of blepharitis.
- Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) Infection: Infection with the herpes simplex virus can cause eye-related complications such as herpetic keratitis, which is inflammation of the cornea. Pregnant women with a history of herpes simplex virus infection may be at risk of experiencing flare-ups during pregnancy due to changes in immune function.
If you experience symptoms of an eye infection during pregnancy, such as redness, irritation, discharge, or vision changes, it is important to consult with an eye care professional or healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment. Some medications commonly used to treat eye infections may not be recommended during pregnancy, so it is essential to seek guidance from a healthcare provider familiar with your medical history and pregnancy status.
How do you treat an eye infection during pregnancy?
Treating an eye infection during pregnancy pregnancy requires careful consideration to ensure the safety of both the mother and the developing fetus. It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider or an eye care professional before starting any treatment, as some medications commonly used to treat eye infections may not be safe during pregnancy. Here are some general guidelines for treating eye infections while pregnant:
- Consult with a Healthcare Provider: If you suspect you have an eye infection, such as conjunctivitis (pink eye), stye, or blepharitis, consult with your healthcare provider or an eye care professional for proper diagnosis and treatment recommendations. They can evaluate your condition and provide guidance on the safest treatment options during pregnancy.
- Use Prescribed Medications: If your healthcare provider determines that medication is necessary to treat the eye infection, they may prescribe topical eye drops or ointments that are considered safe for use during pregnancy. It’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions carefully and use the prescribed medication as directed.
- Avoid Over-the-Counter Medications: While some over-the-counter (OTC) eye drops and ointments may be safe for general use, it’s best to avoid self-medicating with OTC medications during pregnancy without first consulting with a healthcare provider. Some OTC medications may contain ingredients that are not recommended during pregnancy.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Proper hygiene practices can help prevent the spread of eye infections and promote healing. Wash your hands frequently with soap and water, avoid touching or rubbing your eyes, and avoid sharing towels, pillows, or other personal items with others.
- Apply Warm Compresses: For certain types of eye infections, such as styes or blocked oil glands in the eyelids (chalazia), applying warm compresses to the affected eye several times a day may help reduce swelling, promote drainage, and relieve discomfort. Use a clean, warm washcloth and apply gentle pressure to the affected area for 5 to 10 minutes at a time.
- Practice Eye Care: Avoid wearing contact lenses or eye makeup while you have an eye infection, as these can further irritate the eyes or introduce bacteria. If you wear contact lenses, follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations for proper lens care and when it is safe to resume wearing them.
- Follow Up with Healthcare Provider: Keep in touch with your healthcare provider or eye care professional to monitor your condition and ensure that the infection is responding to treatment. If your symptoms worsen or persist despite treatment, seek medical attention promptly.

Conclusion:
Overall, the goal of treating an eye infection during pregnancy is to alleviate symptoms, promote healing, and ensure the safety of both mother and baby. Always seek guidance from a healthcare provider familiar with your medical history and pregnancy status for personalized treatment recommendations.
Recent Post
Stop the Blur? Finding Hope Best Keratoconus Treatment in Thane
Best keratoconus treatment in Thane is now a reality for thousands of patients who previously had to cope with unclear and…
Dr. Anagha Heroor: Cornea Specialist in Thane
Cornea specialist in Thane, Dr. Anagha Heroor, has a rationale of treating patients with empathy, accurate identification, and vision restoration. Light…
Why is Macular Degeneration Surgery in Kalyan Rising?
Macular degeneration surgery in Kalyan is being recognized as a great place for advanced surgery, a condition that is becoming increasingly…